🛠️ What Are “Planning Failures”? 🛠️
In project management, a planning failure (or planning incident) occurs when the actual execution deviates significantly from the planned schedule, cost, resource allocation, or supply chain sequence, leading to negative impacts on the project’s objectives.
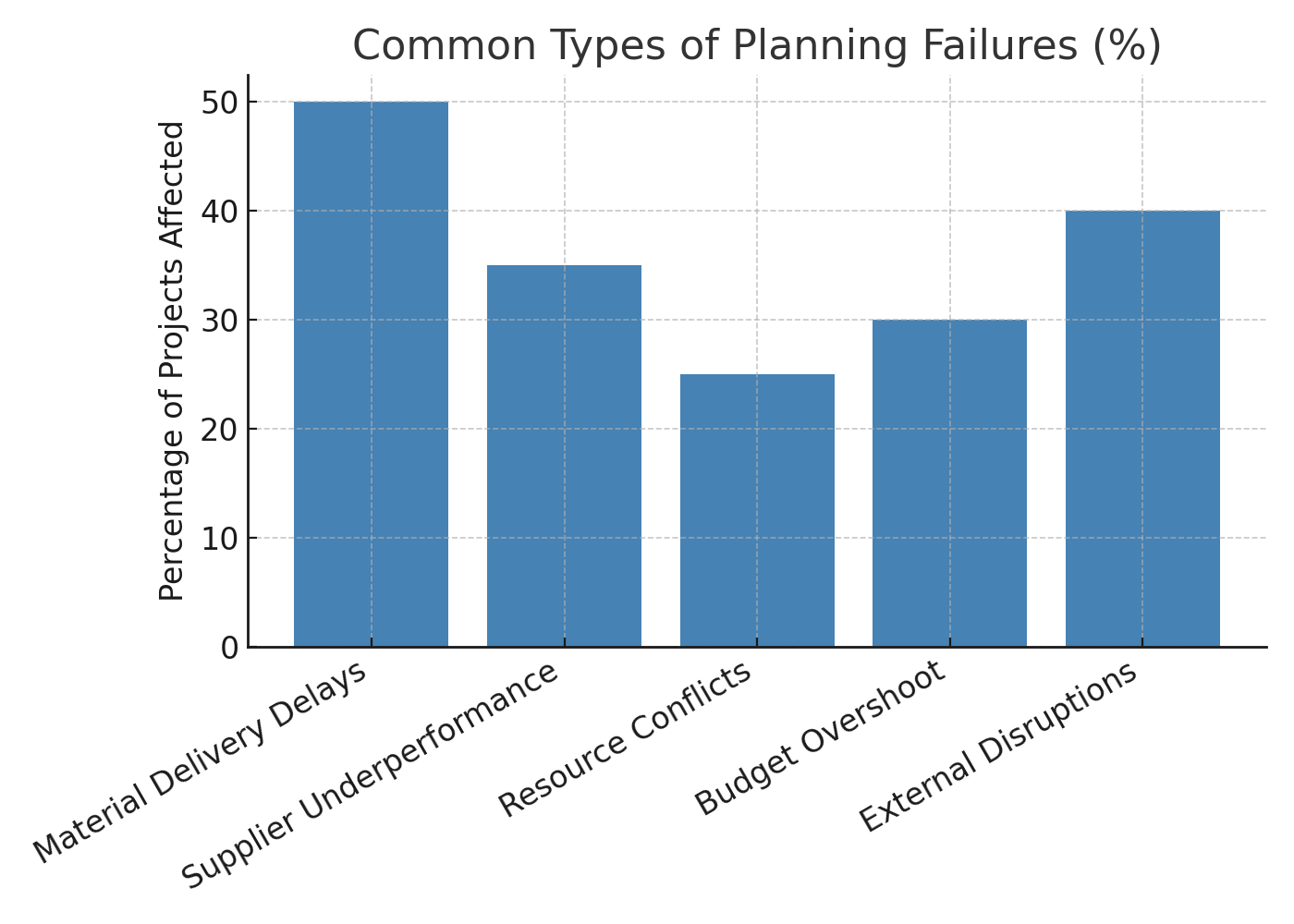
Examples of Planning Failures
- A key material delivery is delayed, cascading downstream delays
- A supplier under-performs, causing inventory shortfall
- Overlapping tasks due to resource conflicts lead to idle time
- Budget overshoot because of unplanned cost escalation
- Unforeseen external disruptions (weather, regulatory hold, transport bottlenecks)
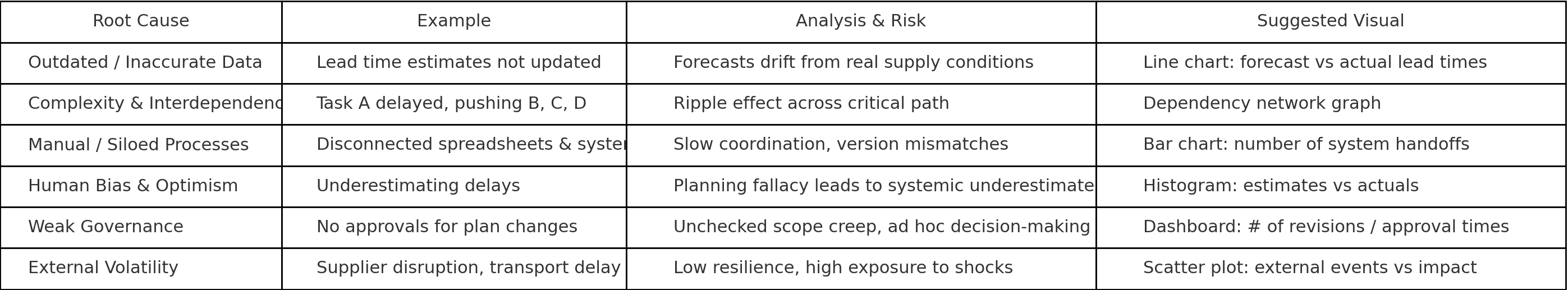
🔎 Root Causes of Planning Failures 🔎
Here are key root causes, with illustrative examples and suggestions for how one might visualize or analyze them:
From academic research, AI and project management integration is becoming more explored. For example, Georgiev et al. (2024) examine the role of AI in project management, especially in supply chain contexts (Taylor & Francis Online). Also, a systematic review of AI in supply chain management shows how AI is applied in forecasting, inventory, logistics, etc., helping reduce disruptions (ScienceDirect).
💡 Solution Proposal: How to Solve Planning Failures Using AI and Management Best Practices 💡
Below is a structured solution framework combining AI tools and governance improvements:
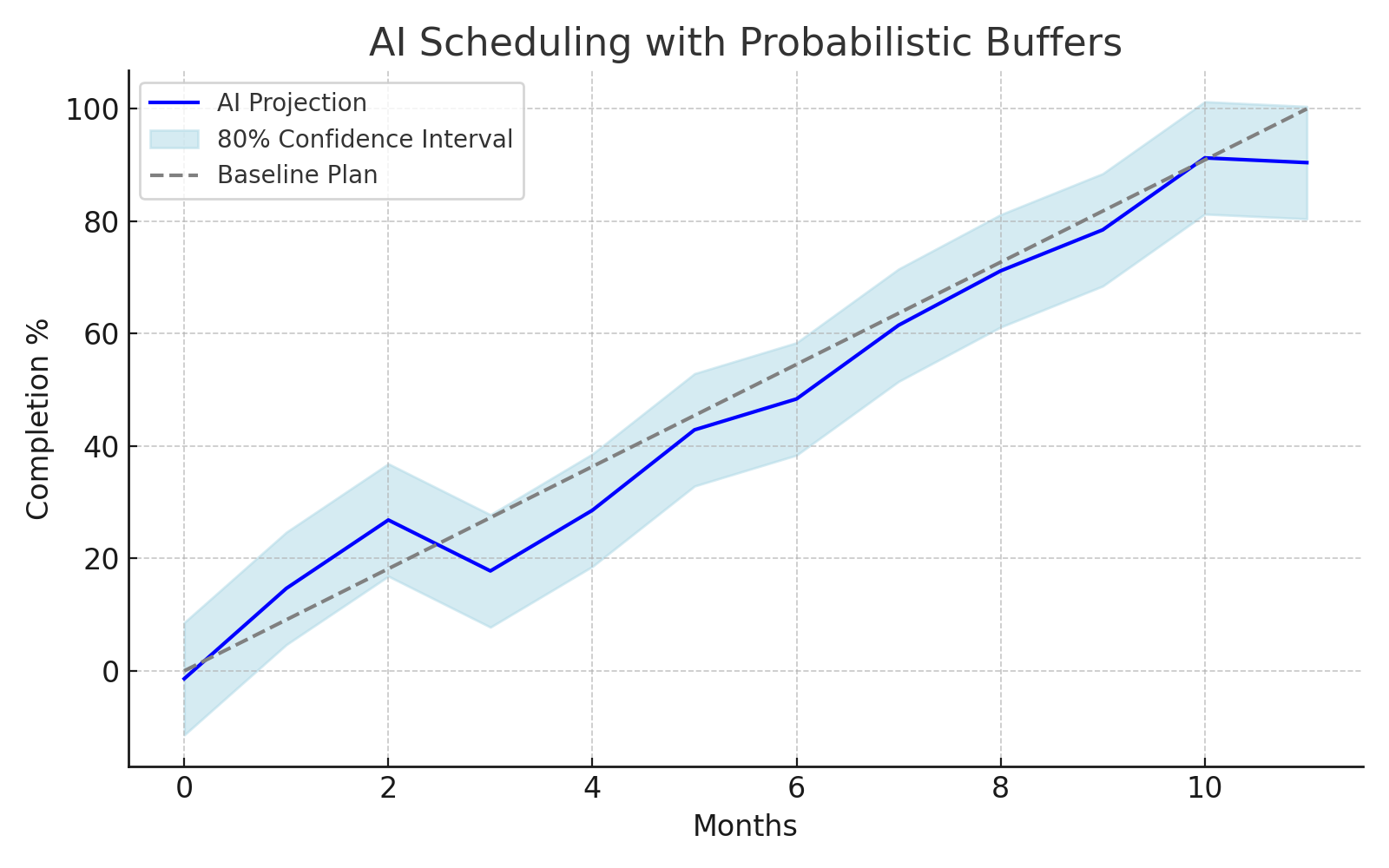
1. ⏱️ Smarter, Adaptive Scheduling (AI-enhanced)
- Use predictive scheduling engines that continuously rerun the critical path based on real-time updates.
- Offer what-if scenario simulations (e.g. supplier X delayed 3 days).
- Show probabilistic buffer margins (i.e. 80% confidence intervals around timeline).
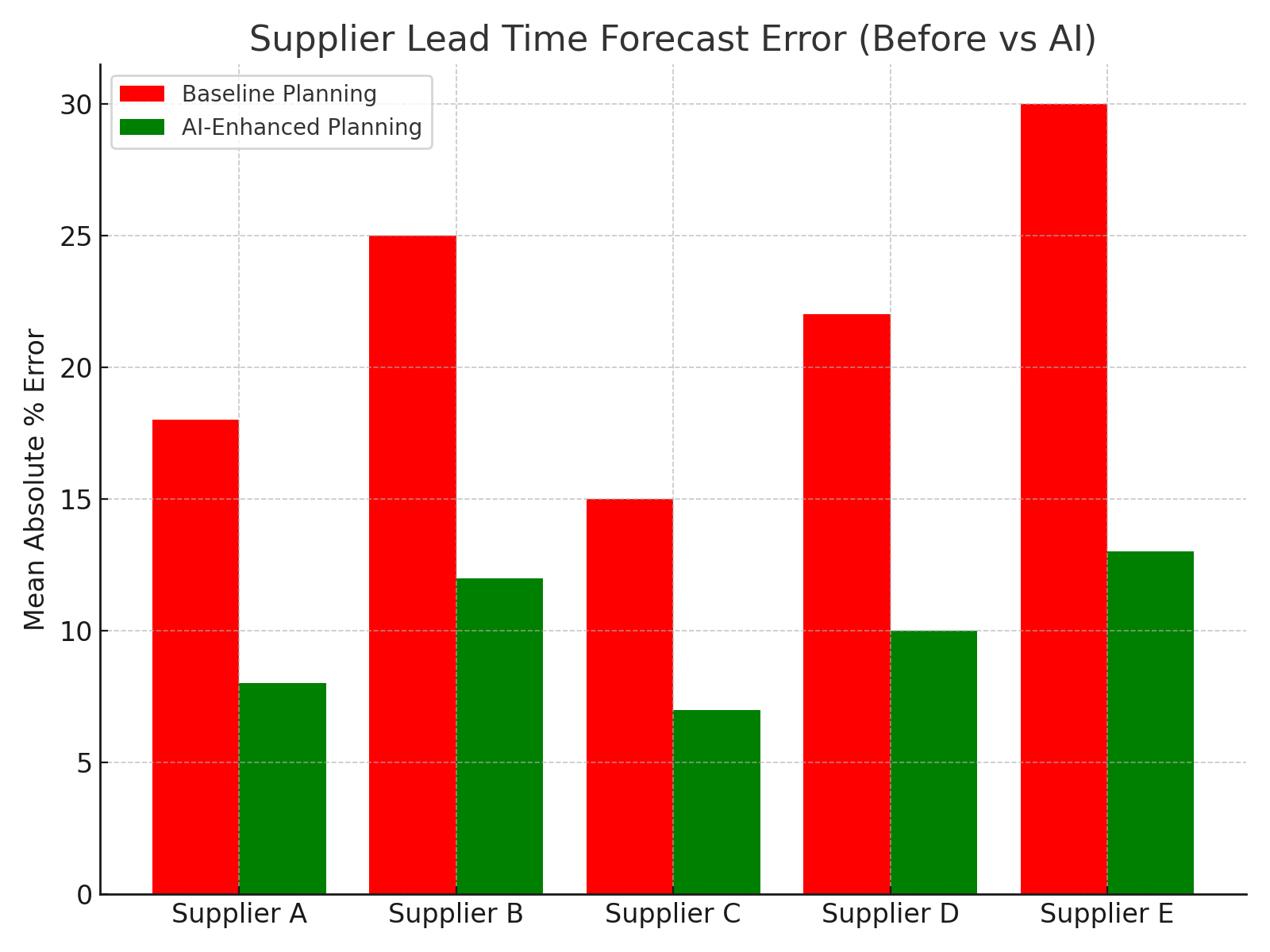
2. 📦 Supply Chain & Demand Forecasting Optimization
- Deploy ML models to forecast demand, lead times, and supplier reliability (ResearchGate).
- Use prescriptive procurement algorithms that suggest staggered orders, buffer stock levels
- Incorporate risk scoring of suppliers (arXiv).
3. 🖥️ Integrated Data & Visibility
- Build data pipelines from ERP, logistics, procurement, and IoT sensors.
- Real-time dashboards showing schedule deviations, resource usage, and supply risk.
- Automated alerts/flags when thresholds exceed limits.
4. 🤖 Decision Support / AI-Assisted Actions
- AI suggests corrective actions: e.g. reassign resources, shift tasks.
- Constraint solvers optimize tradeoffs.
- Natural-language interface: stakeholders can query “What if we delay task 5 by 2 days?”
5. 🏗️ Stronger Governance & Management Oversight
- Establish rules: any delay over X% triggers review.
- Approval workflows for significant plan changes.
- Audit logs and traceability of who changed what and why.
6. 🔄 Continuous Learning & Feedback Loops
- Feed actual outcomes back into models to improve predictions.
- Analyze recurring deviations to detect systemic bias.
- Iterate model retraining and governance policies.
Recent advances even include generative AI planning for supply networks: Ahn et al. (2024) present a “Generative Probabilistic Planning” method using graph neural networks and reinforcement learning to dynamically optimize supply actions across a network (arXiv).
Meanwhile, PROPEL (Akhlaghi et al., 2025) blends supervised learning and reinforcement learning to handle large-scale supply chain planning problems, dramatically reducing search times and gaps.
🛠️ Tutorial: Do YOU want to TEST it? 🛠️
👉 Check out our walkthrough:
🚀 Aden Ready to Bring AI Into Your Project Planning? 🚀
From scheduling with confidence intervals to smarter supply chain forecasting, AI is no longer a future concept - it’s here to reduce overruns, delays, and costly surprises. The teams that adopt these tools today gain a competitive edge tomorrow.
👉 Book a free demo with Aden and see how AI-driven planning can streamline your projects, optimize your supply chain, and keep execution on track -> here.
